
Benefits of Ganoderma lucidum extract on patients with Parkinson’s disease
“Can Ganoderma lucidum relieve the symptoms of patients with Parkinson’s disease?” This is a question that many patients, their families, relatives and friends want to ask.
In a report published in Acta Pharmacologica Sinica in April 2019, the research team headed by Director Biao Chen, Professor of Neurology Department of Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, mentioned that they observed 300 patients with Parkinson’s disease in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial:
These patients ranged from stage 1 (“symptoms appear on one side of the body but do not affect balance”) to stage 4 (“severely impaired mobility but is able to walk and stand independently”). The researchers let the patients take 4 grams of Ganoderma lucidum extract orally every day for 2 years, and found that the patients’ “motor symptoms” can indeed be relieved by the intervention of Ganoderma lucidum.
So-called motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
◆ Tremor: Uncontrollable shaking of limbs.
◆ Limb stiffness: Continuous tightening of muscles due to increased tension, making limbs difficult to move.
◆ Hypokinesia: Slow movement and inability to perform consecutive movements or perform different movements simultaneously.
◆ Unsteady posture: easy to fall due to loss of balance.
Taking Ganoderma lucidum extract every day can slow down the deterioration of these symptoms. Even if there is still a long way to go to cure the disease, it is conceivable that the quality of life of patients with Parkinson’s disease can be improved.


Ganoderma lucidum extract slows the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which is related to the protection of dopamine neurons.
The research team of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University has found through animal experiments that daily oral administration of 400 mg/kg Ganoderma lucidum extract can maintain better motor performance in mice with Parkinson’s disease. The number of dopamine neurons in the brains of mice with Parkinson’s disease is more than double that of mice without Ganoderma lucidum protection (For details, see “Professor Biao Chen’s team from Beijing Xuanwu Hospital confirmed that Ganoderma lucidum protects dopamine neurons and relieves symptoms of Parkinson’s disease”).
Dopamine secreted by dopamine neurons is an indispensable neurotransmitter for the brain to regulate muscle activity. The mass death of dopamine neurons is what causes Parkinson’s disease. Apparently, Ganoderma lucidum slowed the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which was associated with less damage to dopamine neurons.
The root cause of the abnormal death of dopamine neurons is that a large number of toxic proteins have accumulated in the substantia nigra of the brain (the main brain area where dopamine neurons are located). In addition to directly threatening the survival and function of dopamine neurons, these proteins will also activate microglia (immune cells resident in the brain) around nerve cells, causing them to continuously secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines to damage dopamine neurons.
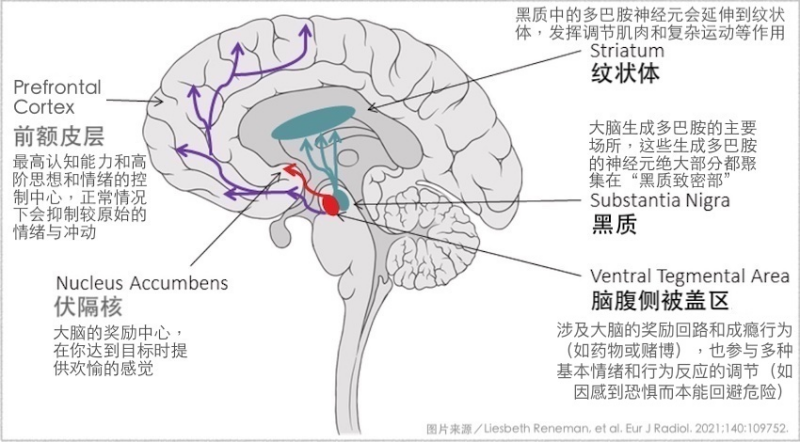
▲The neurons that generate dopamine in the brain are located in the compact part of the “substantia nigra”. The dopamine generated here will be sent to various regions of the brain to play a role along with the extended antennae of the dopamine neurons. The typical movement disorder of Parkinson’s disease is mainly due to the lack of dopamine transported from the substantia nigra to the striatum. Therefore, whether it is dopamine neurons located in the substantia nigra or tentacles of dopamine neurons extending to the striatum, their number and surrounding environment are critical to the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
Previously, the research team of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University has confirmed that Ganoderma lucidum extract can reduce the risk of dopamine neuron damage from the injury-resisting pathway by protecting the mechanism of action of mitochondria (cell generators) in the environment of inflammatory response (For details, see “Professor Biao Chen’s team from Beijing Xuanwu Hospital confirmed that Ganoderma lucidum protects dopamine neurons and relieves symptoms of Parkinson’s disease”).
In September 2022, the team’s research published in Nutrients further confirmed that Ganoderma lucidum extract can reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines through the mechanism of “inhibiting the excessive activation of microglia”, thereby protecting dopamine neurons from the damage-reducing pathway.
Mice with Parkinson’s disease who ate Ganoderma lucidum extract had fewer activated microglia in the substantia nigra and striatum.
According to this newly published report, mice were first injected with neurotoxin MPTP to induce human-like Parkinson’s disease, and then 400 mg/kg of Ganoderma lucidum extract GLE was orally administered every day from the next day (Parkinson’s disease + Ganoderma lucidum extract group) while untreated mice with Parkinson’s disease (only injected with MPTP) and normal mice were used as experimental controls.
After 4 weeks, a large number of activated microglia appeared in the striatum and substantia nigra pars compacta (the main distribution area of dopamine neurons) in the brain of mice with Parkinson’s disease, but this did not happen in the mice with Parkinson’s disease who ate Ganoderma lucidum extract every day – their condition is closer to that of normal mice (pictured below).
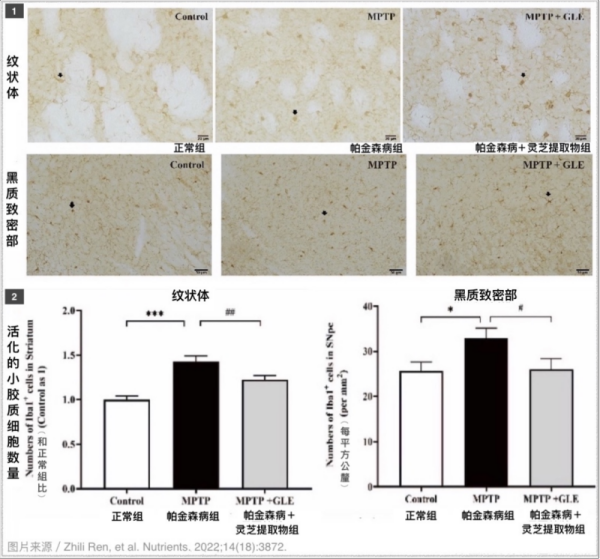
▲ [Description] Ganoderma lucidum has inhibitory effect on microglia in the brain region where the dopamine neurons are located (striatum and substantia nigra pars compacta) in mice with Parkinson’s disease. Figure 1 is the stained image of activated microglia in tissue sections, and Figure 2 is the quantitative statistics of activated microglia.
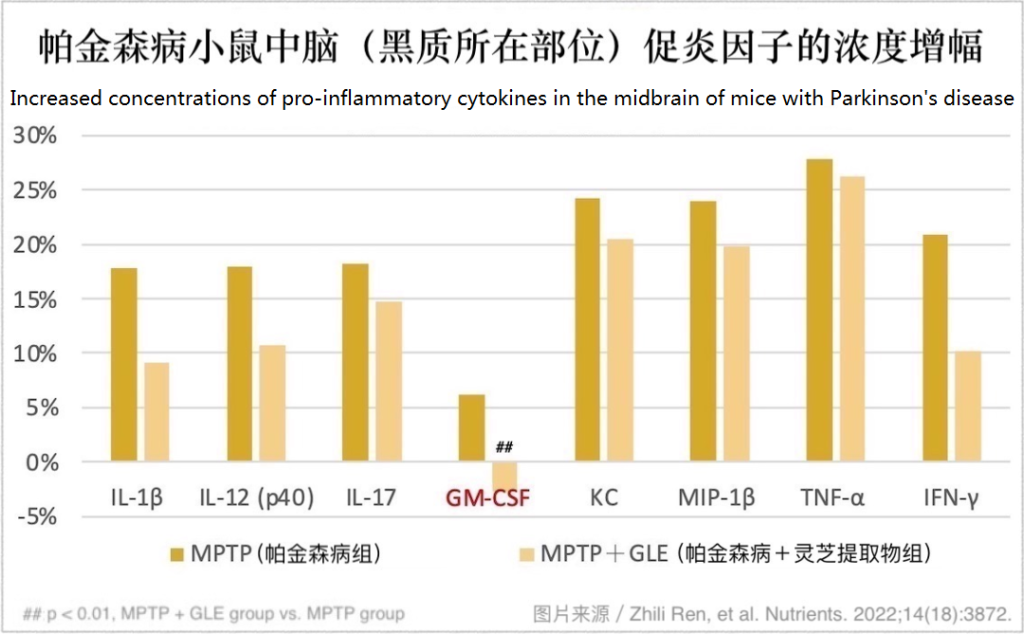
Mice with Parkinson’s disease who ate Ganoderma lucidum extract had lower concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the midbrain and striatum.
Activated microglia cells secrete a variety of cytokines or chemokines to promote inflammation and aggravate the damage of dopamine neurons. However, in the detection of the midbrain and striatum of the above-mentioned experimental animals, the researchers found that daily consumption of Ganoderma lucidum extract can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that are significantly increased due to the onset of Parkinson’s disease (as shown in the figure below).
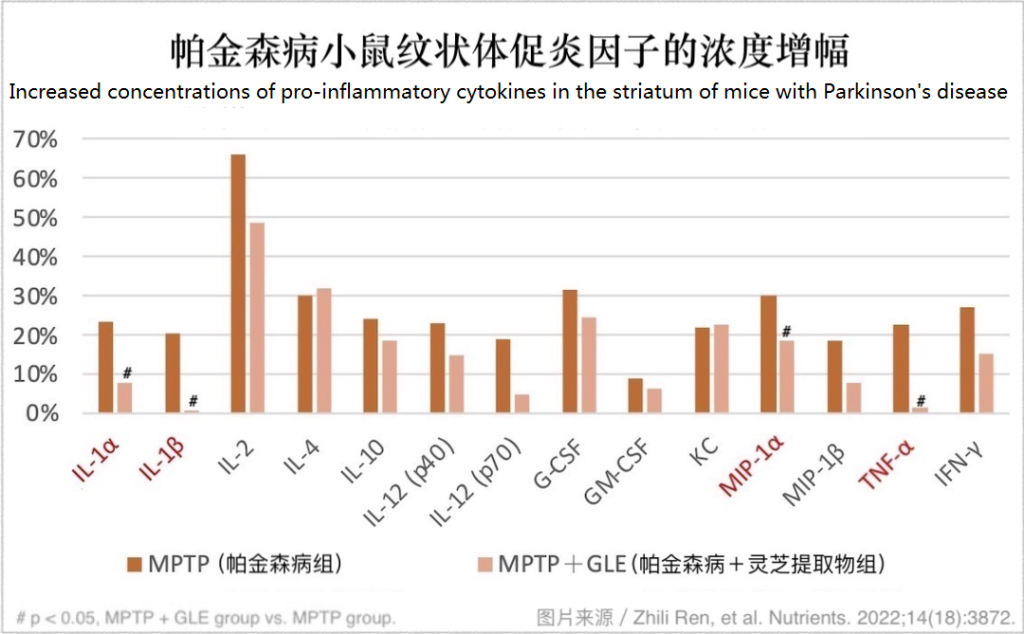
Ganoderma lucidum extract helps delay the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which is the result of the interaction of multiple active ingredients.
The scientific community has confirmed that inflammatory response caused by abnormal activation of microglia is behind the accelerated death of dopamine neurons and the deterioration of Parkinson’s disease. Therefore, inhibition of microglia activation by Ganoderma lucidum extract undoubtedly provides an important explanation for why Ganoderma lucidum extract can alleviate the course of Parkinson’s disease.
What are the components of Ganoderma lucidum that exert these functions?
The Ganoderma lucidum extract GLE used in this research is made from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma lucidum through multiple ethanol and hot water extraction processes. It contains about 9.8% Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, 0.3-0.4% ganoderic acid A (one of the most important triterpenoids in Ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies) and 0.3-0.4% ergosterol.
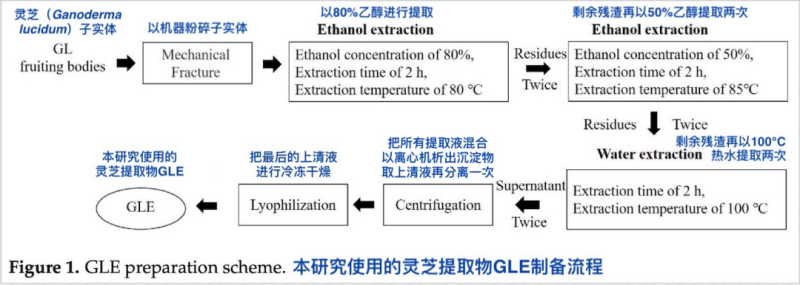
Some related studies in the past have proved that the polysaccharides, triterpenes, and ganoderic acid A in Ganoderma lucidum all have the functions of “regulating inflammatory response” and “protecting nerve cells”. Therefore, researchers believe that the effect of Ganoderma lucidum on delaying the progression of Parkinson’s disease is not the result of the action of a single component but the result of the coordination of multiple components of Ganoderma lucidum in the body.
It may never be clear how the various Ganoderma lucidum components eaten in the stomach cross the “blood-brain barrier” and then exert their effects on the microglia and dopamine neurons in the brain. But in any case, it is an indisputable fact that Ganoderma lucidum components can intervene in the pathogenesis to delay the progression of the disease.
The degeneration of dopamine neurons that causes Parkinson’s disease is not a one-step process but a progressive process that degrades a little every day. Faced with this disease that cannot be ended and can only be marathoned with it for a lifetime, patients can only work harder every day in order to pray for less regression every day.
Therefore, instead of waiting for the new medicine that turns the world around, it is better to seize the time and take the treasure handed down in front of you and try it bravely. It should not be a dream to reproduce the above-mentioned clinical test results summarized from 300 patients by eating a sufficient amount of Ganoderma lucidum for a long time.

Source:
1. Zhili Ren, et al. Ganoderma lucidum Modulates Inflammatory Responses following 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) Administration in Mice. Nutrients. 2022;14(18):3872. doi: 10.3390/nu14183872.
2. Zhi-Li Ren, et al. Ganoderma lucidum Extract Ameliorates MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism and Protects Dopaminergic Neurons from Oxidative Stress via Regulating Mitochondrial Function, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(4):441-450. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0077-8.
3. Ruiping Zhang, et al. Ganoderma lucidum Protects Dopaminergic Neuron Degeneration through Inhibition of Microglial Activation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:156810. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep075.
4. Hui Ding, et al. Ganoderma lucidum extract protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting microglial activation. Acta Physiologica Sinica, 2010, 62(6): 547-554.

★ This article is published under the exclusive authorization of the author, and its ownership belongs to GanoHerb.
★ The above work cannot be reproduced, excerpted or used in other ways without the authorization of GanoHerb.
★ If the work is authorized for use, it should be used within the scope of authorization and indicate the source: GanoHerb.
★ For any violation of the above statement, GanoHerb will pursue the related legal responsibilities.
★ The original text of this article was written in Chinese by Wu Tingyao and translated into English by Alfred Liu. If there is any discrepancy between the translation (English) and the original (Chinese), the original Chinese shall prevail. If readers have any questions, please contact the original author, Ms. Wu Tingyao.



