
GanoHerb Invests Most in Reishi Research
As a writer specializing in the field of Reishi, I have never doubted GanoHerb’s commitment to Reishi scientific research. In fact, just last year (2024), I have written six articles based on GanoHerb’s Reishi research results published in international (4) and domestic (2) journals in collaboration with various academic institutions.
❖ The “Ganoderal B” in Reishi triterpenes inhibits the proliferation and induces apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
(In collaboration with Professor XU Jianhua and Professor LI Peng’s team from the School of Pharmacy, Fujian Medical University)
❖ Reishi spore oil enhances immunity and strengthens the inhibitory effect of chemotherapy drugs on cancer metastasis
(In collaboration with Professor JIA Li’s team from the School of Materials and Chemical Engineering, Minjiang University)
❖ Reishi GanoExtra products enhances the effect of cyclophosphamide in inhibiting lung metastasis of breast cancer in mice while reducing toxicity
(In collaboration with Professor JIA Li’s team from the School of Materials and Chemical Engineering, Minjiang University)
❖ The protective effect of Reishi spore oil, sporoderm-broken spore powder, and spore extract on acute gastric ulcers
(In collaboration with Professor XU Wei’s team from the School of Pharmacy, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine)
❖ “Reishi + Paecilomyces hepiali” for anti-fatigue, “Red Reishi + Purple Reishi” for promoting better sleep
(In collaboration with Professor CHEN Zhuo’s team from the Fujian Institute of Material Structure, Chinese Academy of Sciences)
❖ Triterpenoid Compounds and Hepatoprotective Activity of Antler-Shaped Reishi
(In collaboration with Researcher CHEN Ruoyun and Associate Researcher KANG Jie’s team from the Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences)
These research reports present the specific findings of various academic institutions utilizing their existing experimental platforms to conduct compositional analyses or efficacy validations on a variety of reishi materials provided by GanoHerb.
Since I write articles introducing GanoHerb’s research achievements every year to some extent, I was neither surprised nor taken aback when I came across two recent papers, from different institutions and using different methods to analyze Reishi research trends. Both papers highlighted GanoHerb, a private enterprise, ranking among the top alongside numerous academic and medical institutions in terms of the volume of published Reishi-related research literature. I was not surprised because this recognition is well-deserved, but I was somewhat taken aback by how much further GanoHerb’s investment in research has gone compared to its peers.
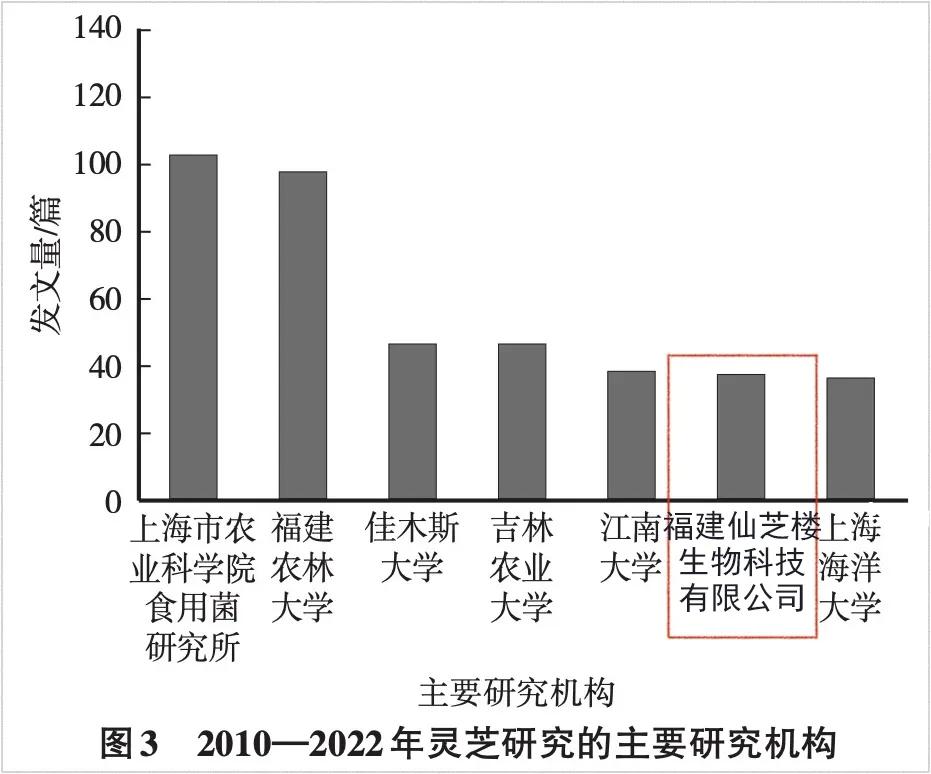
Among the major institutions conducting reishi mushroom research from 2010 to 2022, GanoHerb is the only private enterprise on the list.
The article titled “Analysis of Ganoderma Research Trends Based on Bibliometrics,” published in the second issue of 2024 by the specialized technical journal Edible Fungi, hosted by the Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences, analyzes over 3,000 Chinese-language research papers on Reishi that are available in the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database. These papers, spanning from January 1, 2010, to December 31, 2022, cover topics such as spore powder, spore oil, mycelium, polysaccharides, triterpenoids, and more. One section of the study examined the primary institutions involved in Reishi research, based on the number of publications by the institutions of the authors over these 12 years. The results show that Reishi research in China is predominantly conducted by academic institutions, with six out of the top seven institutions in terms of publication volume being academic. Only one private enterprise made it to the list, which is Fujian Xianzhilou Biological Science and Technology Co., Ltd. See the article screenshots below for more details.
From 1999 to 2020, the publication volume of Chinese literature on Reishi spore powder shows that GanoHerb leads its peers.
In another similar study, a research article titled “Knowledge Graph Analysis of Ganoderma Lucidum Spore Powder Research Based on CiteSpace” was published in the 12th issue of 2021 in Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, a national comprehensive pharmaceutical science and technology journal under the administration of the China Association for Science and Technology and sponsored by the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association. This study analyzed 989 Chinese-language research papers on “Ganoderma lucidum spore powder” retrieved from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database between January 1, 1999, and March 10, 2020. Additionally, the study searched for English-language papers on the same topic in PubMed and Web of Science databases. The following two screenshots present the primary institutions that published these papers. In the second screenshot, the larger the green circle representing an institution and the larger the font size of the institution’s name, the greater the number of publications. Notably, Fujian Xianzhilou Biological Science and Technology Co., Ltd., which is a leader in the field, is prominently featured.


When choosing Reishi, it’s important to select those with a high “scientific research content.”
These two data-driven articles originally focused on analyzing the trends in Reishi research over the past decade or two and its future development. However, they unexpectedly highlighted GanoHerb’s long-term commitment and efforts in Reishi research, bringing it to public attention. It also reminded me of past reports where founders of major smartphone companies emphasized the importance of continuous investment in research and development.
At the launch event for the Xiaomi 10 series, Lei Jun mentioned that Xiaomi’s strategy is to offer high-quality products that meet consumer needs through “technological advancement.” He also emphasized that the company’s long-term success is driven by the fearless “innovation” and “exploration” of Xiaomi’s engineers.
Ren Zhengfei has repeatedly emphasized that Huawei’s survival relies on long-term investment in foundational technology research. This “fundamental research” and “scientific innovation” are the guarantees that enable Huawei to continuously provide high-quality products and services to consumers.
Steve Jobs, who played a key role in creating the iPhone, also said, “Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower.” This means that only companies that actively innovate can continuously design unique and compelling products that elevate the consumer experience, thereby consolidating their market leadership.
The same applies to both mobile phones and Reishi. Whether it is company growth, product upgrades, or meeting the diverse and ever-changing demands of consumers, continuous “pure theoretical research” and “practical scientific innovation” are essential as the driving forces for progress.
Therefore, the depth of a company’s foundation determines its ability to consistently produce high-quality products. As consumers of Reishi who seek “health benefits” rather than just “comfort,” it is better to focus on the company’s dedication to foundational research and scientific innovation, rather than getting caught up in price comparisons or advertising claims.
The number of research papers published to illustrate new scientific achievements and discoveries serves as a concrete indicator of investment in foundational research and scientific innovation. Such an indicator should also serve as a basis for consumers when selecting Reishi products.
References:
- Tian Yi, et al. Analysis of Ganoderma Research Trends Based on Bibliometrics. Edible Fungi, 2024, 46(2): 7-11.
- Zhao Jianxia, et al. Knowledge Graph Analysis of Ganoderma Lucidum Spore Powder Research Based on CiteSpace. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2021, 38(12): 1416-1425.
END

★ This article is exclusively authorized by the author for publication, and its ownership belongs to GanoHerb.
★ The above works cannot be reproduced, excerpted or used in other ways without the authorization of GanoHerb.
★ Those who have been authorized to use the works should use them within the scope of authorization and indicate the source: GanoHerb.
★ GanoHerb will pursue legal responsibilities against those who violate the above statement.
★ The original manuscript of this article was authored in Chinese by Wu Tingyao and subsequently translated into English by Alfred Liu. In the event of any inconsistencies between the English translation and the original Chinese text, the latter shall take precedence. For any queries, pls reach out to the original author, Ms. Wu Tingyao.




