أبريل 12, 2017 / جامعة براويجايا / القلب الدولية
نص / وو تينغ ياو
النظام الغذائي طويل الأمد الذي يحتوي على نسبة عالية من الكوليسترول يمكن أن يؤدي بسهولة إلى ارتفاع نسبة الدهون في الدم بشكل غير طبيعي, ويمكن أن تؤدي نسبة الدهون غير الطبيعية في الدم على المدى الطويل إلى تصلب الشرايين. لكن, لوغانوديرما لوكيدوم يتم التدخل في السكريات, حتى لو كانت نسبة الدهون في الدم لا تزال غير طبيعية, ومن المرجح أن ينخفض خطر الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين.
نشرت منظمة "القلب الدولية" تقريرا من جامعة براويجايا في إندونيسيا في 2017, إثبات ذلكغانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد (الغني بالبروتين β-D-glucan المستخرج منغانوديرما لوكيدوم) يكون لها هذا التأثير الوقائي.
تأثيرات متعددة ضد تصلب الشرايين
وقام الباحثون بإطعام الفئران بنظام غذائي عالي الكولسترول 12 أسابيع. تم تغذية ثلاث مجموعات من الفئران في وقت واحد مع انخفاض, جرعات متوسطة وعالية (50, 150, 300 ملغم/كغم) ofغانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد (شرطة الأمن العام) تحضير, الذي يحتوي على 20%غانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد, في الاخير 4 أسابيع من التجربة.
بعد التجربة, وتم تحليل صحة الأوعية الدموية لدى الفئران من خلال أربعة مؤشرات, وتم التوصل إلى النتائج التالية فيما يتعلق بالفئران التي أكلتغانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد:
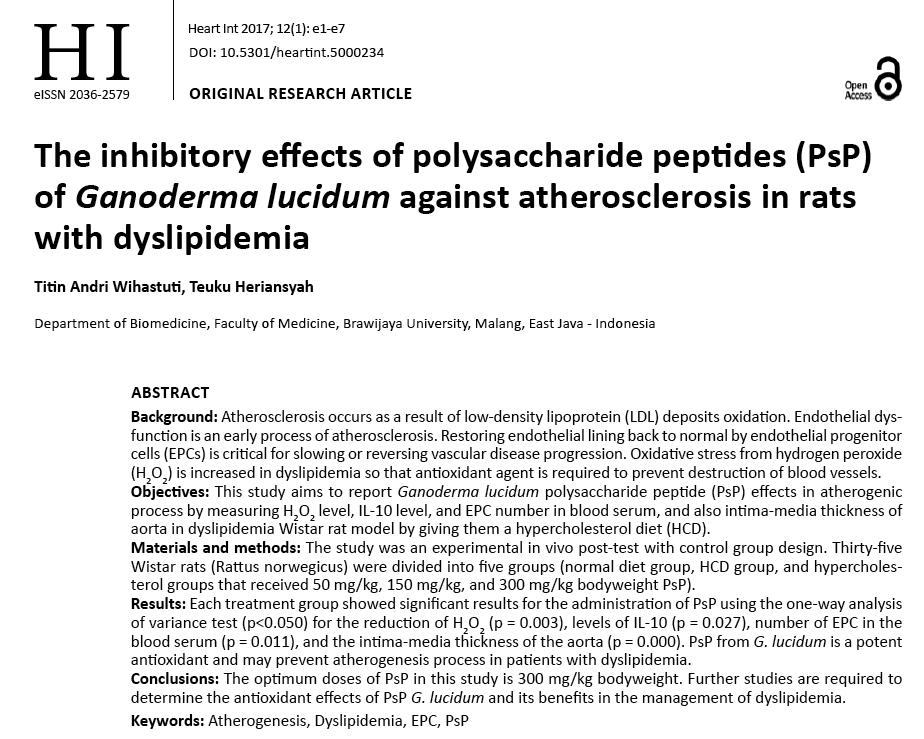
1. تركيز الجذور الحرة H2O2 في المصل أقل بكثير - كوليسترول البروتين الدهني منخفض الكثافة (LDL-C) يتأكسد المتراكم في جدار الأوعية الدموية بواسطة الجذور الحرة, وهي الخطوة الأولى في تكوين تصلب الشرايين. عندما تنخفض الجذور الحرة, تقل فرصة الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين بشكل طبيعي.
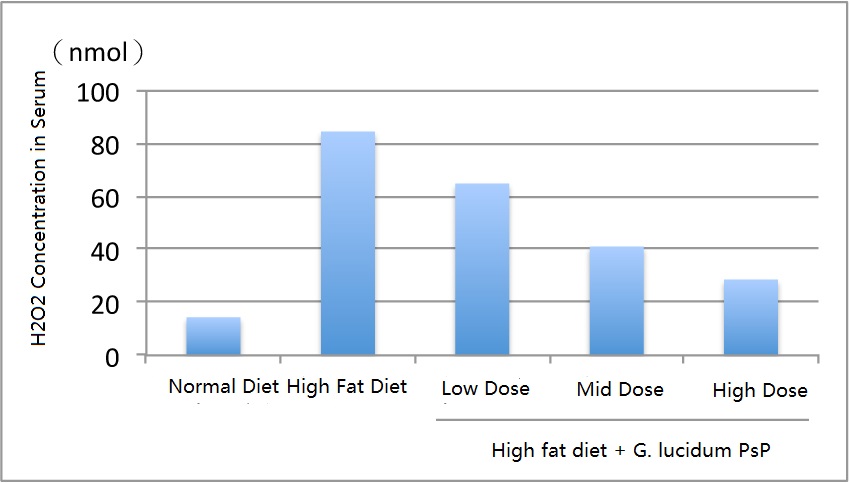
2. إفراز IL-10, السيتوكين المضاد للالتهابات, يتم تقليله - وهذا يعني أن درجة الالتهاب خفيفة, لذلك ليست هناك حاجة لكمية كبيرة من الإنترلوكين 10 لمحاربة الالتهاب.
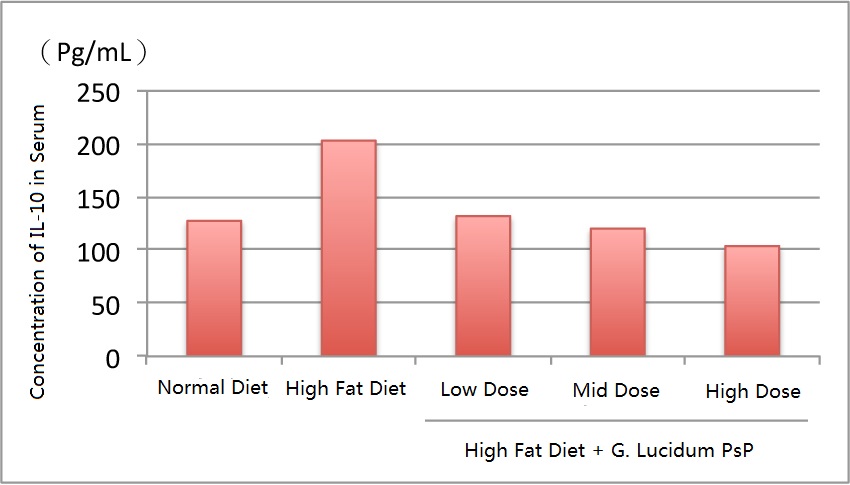
3. لقد زاد عدد "الخلايا السلفية البطانية" التي يمكن استخدامها لإصلاح جدران الأوعية الدموية التالفة - يمكن للخلايا السلفية البطانية التي تنتشر في جميع أنحاء الجسم بالدم إصلاح جدران الأوعية الدموية المتضررة بسبب الأكسدة والالتهاب. لذلك, تشير زيادة الخلايا السلفية البطانية إلى زيادة إمكانية إصلاح جدار الأوعية الدموية التالفة, وتقل نسبيًا فرصة التطور إلى تصلب الشرايين.
4. سمك الجدار الداخلي للشريان الأورطي (الحميمة ووسائل الإعلام) قريب من الطبيعي - يمكن تقسيم المقطع العرضي للأوعية الشريانية إلى ثلاث طبقات من الداخل إلى الخارج: يسمى جدار الوعاء الدموي المتصل بتدفق الدم بالبطانة, والتي تتكون من الخلايا البطانية; الطبقة الوسطى المكونة من العضلات الملساء تسمى الوسائط. هاتان الطبقتان من الأنسجة الوعائية هما أهم مناطق الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين. لذلك, عندما يكون سمك الطبقتين أقرب إلى الطبيعي, فهذا يعني أن الشرايين في حالة صحية نسبيًا.
تركيز الجذور الحرة في مصل الفئران
[ملحوظة] H2O2 هو نوع من الجذور الحرة. كلما قل تركيزه, كلما قل احتمال الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين. (الرسم / وو تينغ ياو, مصدر البيانات/القلب كثافة العمليات. 2017; 12(1): e1-e7.)
تركيز السيتوكين المضاد للالتهابات في مصل الفئران
[ملحوظة] عندما لا يكون تركيز IL-10 المضاد للالتهابات في المصل مرتفعًا جدًا, فهذا يعني أن التهاب جدار الأوعية الدموية قد لا يكون شديدًا, ويتم أيضًا تقليل خطر الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين. (الرسم / وو تينغ ياو, مصدر البيانات/القلب كثافة العمليات. 2017; 12(1): e1-e7.)
عدد الخلايا السلفية البطانية في دم الفئران
[ملحوظة] يمكن للخلايا السلفية البطانية إصلاح جدران الأوعية الدموية التالفة. عندما يزيد عددهم, فهذا يعني أن خطر الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين قد انخفض أو يمكن تأخيره. (الرسم / وو تينغ ياو, مصدر البيانات/القلب كثافة العمليات. 2017; 12(1): e1-e7.)
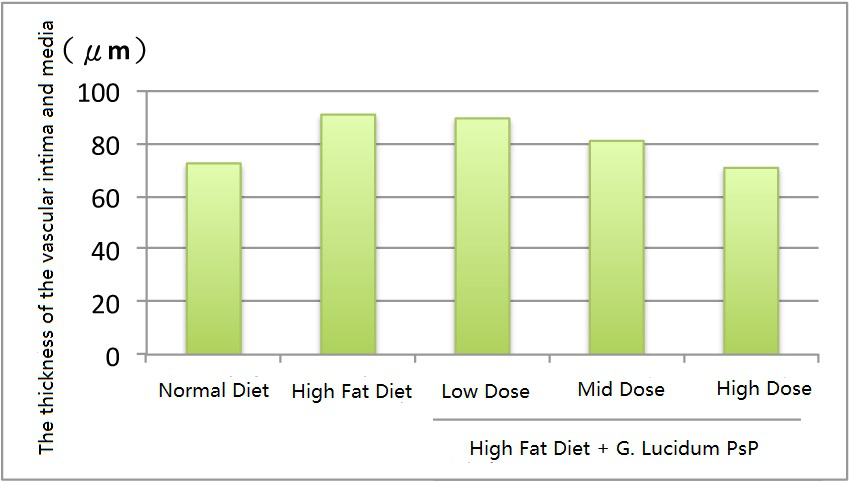
سمك الجدار الشرياني للفئران
[ملحوظة] تعد "البطانة الداخلية" و"الوسائط" الوعائية من أهم مناطق الإصابة بتصلب الشرايين. كلما كان سمكها أقرب إلى سمك الشرايين في ظل النظام الغذائي العادي, كلما كانت الأوعية الدموية أكثر صحة.(الرسم / وو تينغ ياو, مصدر البيانات/القلب كثافة العمليات. 2017; 12(1): e1-e7.)
حمايةغانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد على نظام القلب والأوعية الدموية قد لا تنعكس بشكل كامل في المؤشرات المرئية.
التجارب المذكورة أعلاه تبين أنه على الرغم من أن سبب تصلب الشرايين (نظام غذائي عالي الدهون) لا يزال موجودا, ولا تزال نسبة الدهون في الدم غير طبيعية, غانوديرما لوكيدوم يمكن للببتيدات متعددة السكاريد أن تحافظ على الأوعية الدموية الشريانية في حالة صحية نسبيًا من خلال التأثيرات الثلاثية لمضادات الأكسدة, مضاد للالتهابات وتحسين فرصة إصلاح جدران الأوعية الدموية التالفة. ومفعولغانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد تتناسب مع جرعتها.
لأن فريق البحث سبق أن أكد من خلال الدراسات السريرية أن استخدام ذلكغانوديرما لوكيدوم يمكن أن يؤدي تحضير الببتيدات عديدة السكاريد للعلاج المساعد للمرضى الذين يعانون من الذبحة الصدرية إلى تحسين الالتهاب بشكل كبير, الضرر التأكسدي, سكر الدم, والدهون في الدم في الجسم, وبالتالي تقليل وتيرة وشدة الذبحة الصدرية. لذلك, إمكانات التطبيق السريري للغانوديرما لوكيدوم الببتيدات السكاريد تستحق بالفعل توقعاتنا.
استخدمت العديد من الدراسات في الماضي "خفض نسبة الدهون في الدم إلى وضعها الطبيعي" كمؤشر محدد لفعاليةغانوديرما لوكيدوم في حماية نظام القلب والأوعية الدموية. لكن, يخبرنا بحث من إندونيسيا أنه حتى لو لم تعد نسبة الدهون في الدم إلى وضعها الطبيعي, أو حتى في حالة استمرار حدوث الذبحة الصدرية, لا ينبغي لنا أن نشعر بخيبة أملغانوديرما لوكيدوم لأنه كان يعمل, لكن قد لا تتمكن من رؤية تأثيره بأم عينيك. طالما يتم تناوله كثيرًا ولفترة طويلة, حمايةغانوديرما لوكيدوم على نظام القلب والأوعية الدموية سوف تستمر.
[مصدر البيانات] ويهاستوتي تا, وآخرون. التأثيرات المثبطة للببتيدات السكاريد (شرطة الأمن العام) جانوديرما لوكيدوم ضد تصلب الشرايين في الجرذان المصابة بخلل شحوم الدم. كثافة العمليات القلب. 2017; 12(1): e1-e7.
END
نبذة عن الكاتبة/ م. وو تينغياو
وقد ظل وو تينغ ياو يقدم تقارير عن معلومات الجانوديرما المباشرة منذ ذلك الحين 1999. هي مؤلفة الشفاء بالجانوديرما (نشرت في دار النشر الطبية الشعبية في أبريل 2017).
★ يتم نشر هذه المقالة بموجب التفويض الحصري للمؤلف.
★ لا يمكن إعادة إنتاج الأعمال المذكورة أعلاه, مقتطفة أو مستخدمة بطرق أخرى دون إذن المؤلف.
★ لانتهاكات البيان أعلاه, سوف يتابع المؤلف المسؤوليات القانونية ذات الصلة.
★ تمت كتابة النص الأصلي لهذه المقالة باللغة الصينية بواسطة Wu Tingyao وترجمها إلى الإنجليزية بواسطة Alfred Liu. إذا كان هناك أي اختلاف بين الترجمة (إنجليزي) والأصل (الصينية), يجب أن تسود الصينية الأصلية. إذا كان لدى القراء أي أسئلة, يرجى الاتصال بالمؤلف الأصلي, آنسة. وو تينغياو.



