6月 15, 2018 / 慶尚大学校, 韓国 / Journal of Clinical Medicine
文/呉廷耀

韓国の京都国立大学医学部6月に臨床医学のジャーナルに論文を発表した 2018 それを述べるマンネンタケ 高脂肪食によって引き起こされる肝臓脂肪の蓄積を減らすことができます, しかし、関連する動物実験では、マウスが高脂肪食によって肥育したことも、の介入により血糖と血液の脂質の問題が少ないことも発見しました。マンネンタケ.
実験マウスは4つのグループに分けられました: 通常の食事 (ND), 通常の食事 (ND) + マンネンタケ (GL), 高脂肪食 (HFD), 高脂肪食 (HFD) + マンネンタケ (GL). 通常のダイエットグループの飼料で, 脂肪が説明されました 6% 総カロリーの; 高脂肪食の餌, 脂肪が説明されました 45% 総カロリーの, それはそうでした 7.5 前者の時代. のマンネンタケ マウスに給餌することは、実際には結実体のエタノール抽出物ですマンネンタケ. 研究者は、マウスを投与して給餌しました 50 mg/kgマンネンタケ 1日あたり週5日、エタノール抽出物.
16週間後 (4か月) 実験の, 長期的な高脂肪食はマウスの重量を2倍にできることがわかった. 彼らが食べてもマンネンタケ, 体重を増やす傾向をブロックすることは困難です (形 1).
しかし, 高脂肪食の前提の下で, 食べるマウスマンネンタケ そして、食べないマウスマンネンタケ 同様のレベルの肥満があるように見えます, 彼らの健康状態は、食べるか食べていないためにかなり異なりますマンネンタケ.
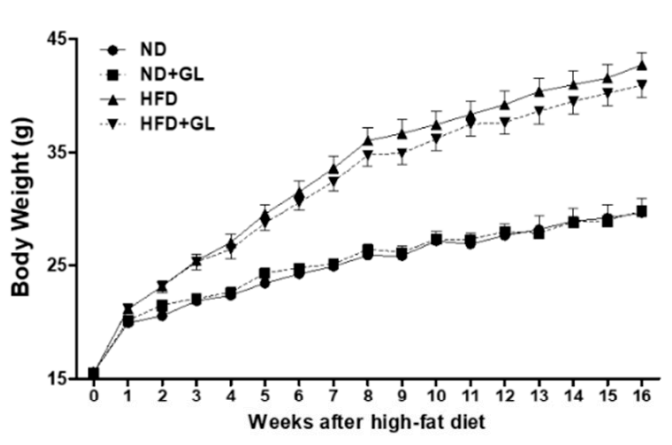
図1 の効果マンネンタケ HFD給電マウスの体重
マンネンタケ HFD給電マウスの内臓脂肪蓄積を減らします.
形 2 肝臓の外観と重量の統計図です, 実験の終わりにおけるマウスの各グループの周囲脂肪と精巣上体脂肪.
肝臓は体内の栄養加工植物です. 腸から吸収されたすべての栄養素が分解されます, 肝臓によってセルが使用できる形式に合成および処理された, そして、血液循環を通してどこにでも分布しました. 供給過剰があります, 肝臓は過剰なカロリーを脂肪に変換します (トリグリセリド) 緊急事態のために保管してください.
より多くの脂肪が保存されます, 肝臓が大きくて重いほど. もちろん, 過剰な脂肪も他の内臓の周りに蓄積します, そして、周囲脂肪と精巣上体脂肪は、動物実験で観察された内臓脂肪蓄積の代表です.
図からわかります 2 それマンネンタケ 高脂肪食によって引き起こされる肝臓や他の内臓の脂肪の蓄積を大幅に減らすことができます.
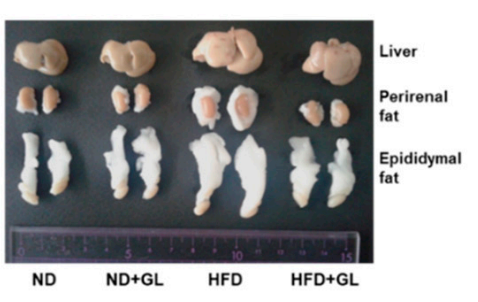
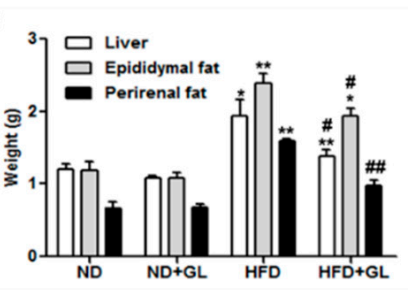
図2 の効果マンネンタケ HFDフィードマウスの内臓脂肪について
マンネンタケ HFD給餌マウスの脂肪肝を減少させる.
研究者らはさらに、マウスの肝臓の脂肪含有量を分析した。: 各グループのマウスの肝臓組織切片を特殊な染料で染色しました。, 肝臓組織の油滴は色素と結合して赤くなります. 図に示すように 3, 肝臓の脂肪含有量は、同じ高脂肪食でも、添加物を添加した場合と添加しない場合で大きく異なりました。マンネンタケ.
各グループのマウスの肝臓組織の脂肪を図に定量化しました。 4, 高脂肪食グループの脂肪肝はグレードに達していることがわかりました。 3 (脂肪含有量は以上でした 66% 肝臓全体の重さ, 重度の脂肪肝を示す). 同時に, HFDを与えて食べたマウスの肝臓の脂肪含有量マンネンタケ 半分に減りました.
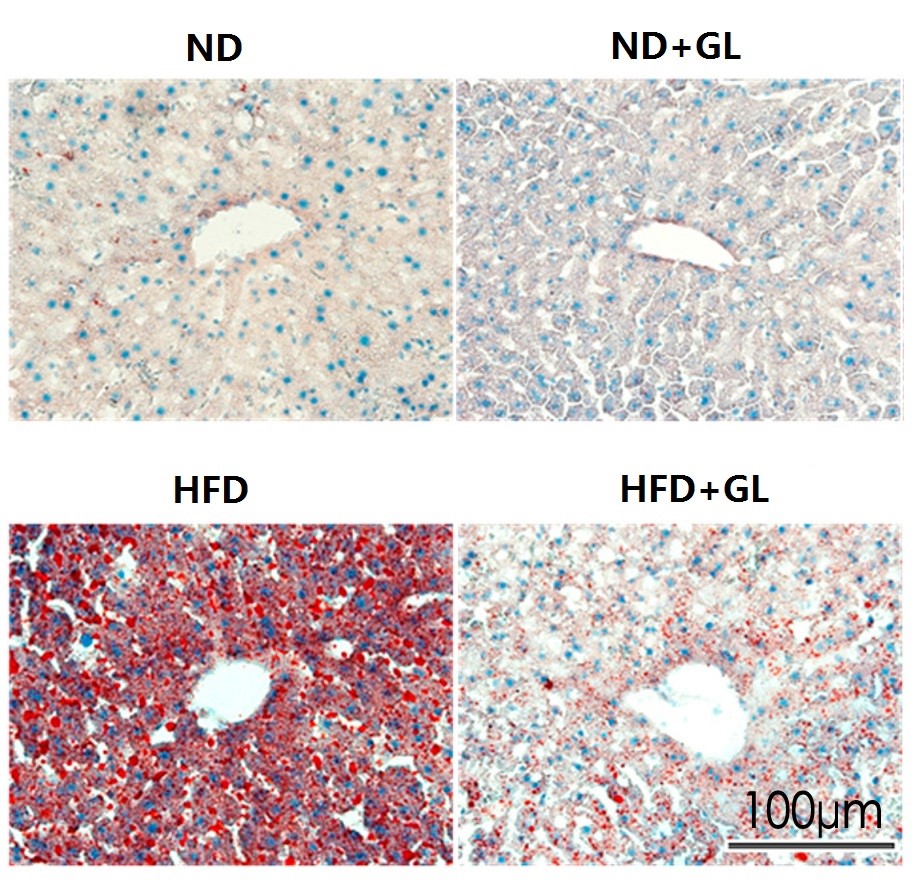
図3 マウス肝臓組織切片の脂肪染色結果
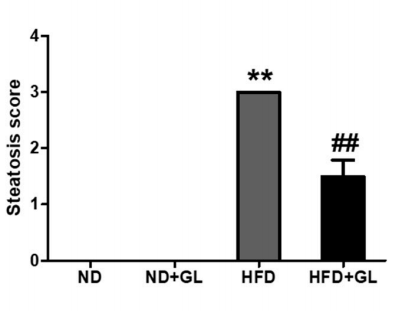
図4 の効果マンネンタケ HFD給電マウスの肝臓脂肪の蓄積について
[説明] 脂肪肝臓の重症度はグレードに分類されました 0, 1, 2, そして 3 肝臓の体重の脂肪重量の割合に応じて: 未満 5%, 5-33%, より多い 33%-66% そしてそれ以上 66%, それぞれ. 臨床的意義は正常を表しています, 軽度, 中程度で重度の脂肪肝臓.
マンネンタケ HFD給電マウスの肝炎を防ぎます.
過度の脂肪の蓄積は肝臓のフリーラジカルを増加させます, 酸化的損傷のために肝臓細胞を炎症にかけがちなものにする, それにより、肝機能に影響します. しかし, すべての脂肪肝臓が肝炎のレベルに進むわけではありません. 肝臓細胞が過度に損傷していない限り, それらは、比較的無害な「単純な脂肪蓄積」で維持できます。
図からわかります 5 高脂肪食は血清ALTを二重にできること (gpt), 肝炎の最も重要な指標, 通常レベルくらいから 40 U/L; しかし, もしマンネンタケ 同時に取られます, 肝炎の可能性は大幅に減少します. 明らかに, マンネンタケ 脂肪に浸潤した肝細胞を保護する効果があります.
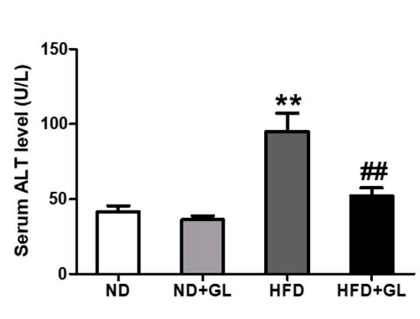
図 5 の効果マンネンタケ HFDを与えたマウスの肝炎指数について
マンネンタケ HFDを与えられたマウスの血中脂質の問題を軽減します.
肝臓で脂肪が過剰に合成されると、, 血中脂質も異常を起こしやすい. 韓国で行われたこの動物実験では、4か月間高脂肪食を摂取するとコレステロールが上昇する可能性があることが判明した, しかしマンネンタケ 問題の重大度を軽減できる (形 6).
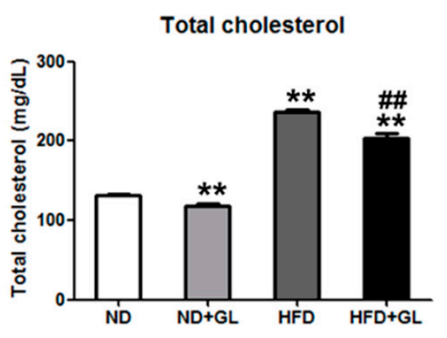
図6 の効果マンネンタケ HFD給餌マウスの血清総コレステロールに及ぼす影響
マンネンタケ HFDを与えられたマウスの血糖上昇を抑制します.
高脂肪食は血糖値を上昇させる可能性があることも実験で判明. しかし, もしマンネンタケ 同時に取られます, 血糖値はわずかな上昇で明らかに制御できる (形 7).
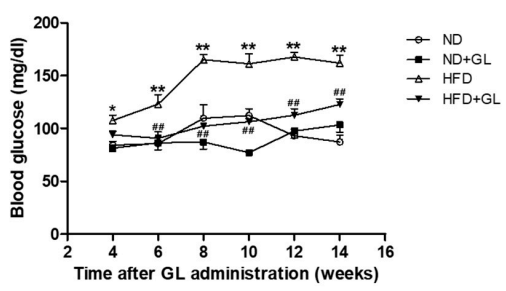
図7 の効果マンネンタケ HFD給餌マウスの血糖値の変化
マンネンタケ HFDを与えられたマウスの血糖を調節する能力を改善します。.
研究者らは実験の14週目にマウスの耐糖能試験も実施した。, つまり, その後の絶食状態で 16 何時間もの断食, マウスには大量のブドウ糖が注射された, 2時間以内の血糖変化が観察された. 血糖値の変動が小さいほど, マウスの体の血糖調節能力が優れているほど.
HFDの血糖値の変動は、 + GL群はHFD群より低かった (形 8). これはつまり、マンネンタケ 高脂肪食による血糖調節を改善する効果がある.
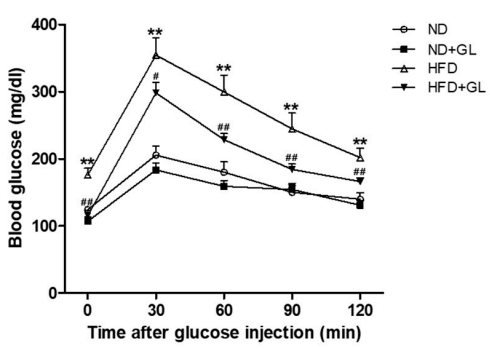
図8 の効果マンネンタケHFD給餌マウスの耐糖能に関する研究
マンネンタケ HFDを与えられたマウスのインスリン抵抗性を改善する.
研究者らはマウスのインスリン耐性試験も実施した: 実験の14週目で, 絶食マウスにインスリンを注射した, 血糖値の変化は、インスリンに対するマウスの細胞の感受性を決定するために使用されました。.
インスリンはホルモンです, 鍵の役割を果たすのは, 食物中のブドウ糖が血流から体の細胞に入り、エネルギーを生成できるようにします。. 通常の状況では, インスリン注射後, 本来の血糖値はある程度下がります. インスリンの働きにより、より多くの血糖が細胞内に入るからです。, 血糖値は自然に下がります.
しかし, 実験の結果は、長期の高脂肪食が細胞をインスリンに鈍感にするため、インスリン注射後に血糖値が高いままであることがわかったことがわかりました。, しかし同時に, HFD給電マウスの血糖変動は食べましたマンネンタケ Nd-Fedマウスのそれに似ていました (形 9). それは明らかですマンネンタケ インスリン抵抗性を改善する効果があります.
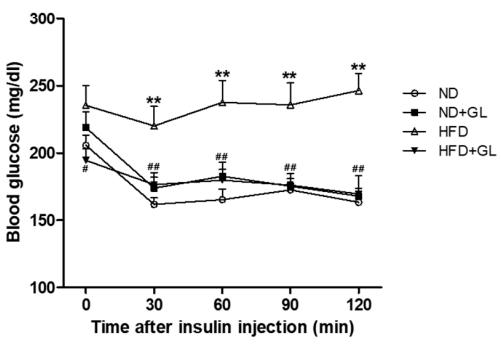
図9 の効果マンネンタケ HFD給電マウスのインスリン抵抗性について
の仕組みマンネンタケ 脂肪肝臓の減少において
肥満はインスリン抵抗性を誘発する可能性があります, インスリン耐性は高血糖を引き起こすだけでなく、非アルコール性脂肪肝につながる最も重要な要因でもあります. したがって, インスリン抵抗性が減少する場合マンネンタケ, 肝臓は当然、脂肪の蓄積を起こしやすいです.
加えて, 研究者はまた、エタノール抽出物を確認しましたマンネンタケ 動物実験で使用される結実体は、肝臓の脂質代謝に関与するいくつかの酵素の活性を直接調節するだけでなく、肝細胞による脂肪の合成を直接阻害することもできます。, 効果は投与量に比例しますマンネンタケ. さらに重要なことは, これらの効果的な用量の後マンネンタケ 人間の肝細胞で培養されました 24 hours, 細胞はまだ生きていて元気でした.
マンネンタケ 血糖を下げることの影響があります, 脂肪を下げ、肝臓を保護します.
上記の研究結果は、のアルコール抽出物がマンネンタケ 結合体は、高血糖の症状を軽減する可能性があります, 高脂血症, そして、高脂肪食によって引き起こされる脂肪肝.
薬で, 非アルコール性要因によって引き起こされる脂肪肝を総称して「非アルコール性脂肪肝」といいます。他にも考えられる要因はありますが、 (麻薬などの), 食生活と生活習慣が依然として最も一般的な原因です. フォアグラがどうやって作られるのか考えてみましょう, 食いしん坊に愛されている, 作られています? それは人も同じです!
統計によると, 成人のほぼ 3 分の 1 が単純な症状を持っています。 (つまり, 肝炎の症状がない) 非アルコール性脂肪肝, そしてそのうちの約4分の1は15年以内にさらに脂肪性肝炎に進行します。. 台湾では非アルコール性脂肪肝がALT指数異常の主な原因となっているという報告もある (33.6%), B型肝炎ウイルスをはるかに上回る (28.5%) そしてC型肝炎ウイルス (13.2%). (参考資料を参照 2 詳細については)
皮肉なことに, 世界の保健機関がワクチンや治療薬でウイルス性肝炎と闘い続ける中, 食べすぎや飲みすぎによって引き起こされる脂肪肝疾患の有病率が増加しています.
脂肪肝疾患 (脂肪症) 肝臓の脂肪がそれに達するかそれを超えると発生します 5% 肝臓の重さ. 脂肪肝疾患の初期診断は、腹部超音波検査またはコンピューター断層撮影に頼らなければなりません (CT). 健康診断を受ける習慣がついていない方, 中等度の肥満などのメタボリックシンドロームの有無から脂肪肝かどうかを判断することもできます, 高血糖 (タイプ 2 糖尿病) これらの症状や疾患は非アルコール性脂肪肝疾患と一緒に起こることが多いため、高脂血症が考えられます。 (NAFLD).
ただ、脂肪肝に効く特効薬はありません. これが理由です, 脂肪肝と診断されてから, 医者はあなたに軽い食事しか処方できません, 積極的な治療ではなく運動と減量. しかし, 食生活や生活習慣を変えるのは簡単ではありません. ほとんどの人は、「食事管理や運動量の増加に失敗する」という泥沼にはまってしまうか、「食事管理や運動量を増やしても脂肪肝が治らない」という苦悩のどちらかに陥っています。.
一体どうすればいいのか? 韓国慶尚大学校の研究結果を読んで, 私たちは別の魔法の武器があることを知っています, つまり, エタノール抽出物を食べるマンネンタケ 子実体.
マンネンタケ, 肝臓を保護する働きがある, 血糖値を下げる, そして脂肪を減らす, 本当に費用対効果が高いです; それでも痩せることはできませんが、, たとえ肥満であっても少なくとも健康になる可能性はある.
[ソース]
ジョン・S, 他. マンネンタケ 肝臓のエネルギー代謝酵素を上方制御することにより、非アルコール性脂肪症を改善します. J Clin with. 2018 ジュン 15;7(6). pii: E152. 土肥: 10.3390/JCM7060152。
[さらに読む]
偶然にも, 早く 2017, レポート「抗糖尿病活性マンネンタケ 多糖類F31糖尿病マウスにおける肝臓グルコース調節酵素のダウンレギュレートされた」は、広州微生物学研究所と疾病管理予防のための広東省の地方センターが共同で公開しました。. タイプの動物モデルに基づいています 2 糖尿病, の規制メカニズムを調査しますマンネンタケ 血液グルコースに対する実体活性多糖類と糖尿病によって引き起こされる肝炎の予防と治療. その作用メカニズムは、肝臓のエネルギー代謝に関与する酵素の調節とインスリン抵抗性の改善にも関連しています. それとこの韓国の報告書は、異なる手段によって同じ端に到着します. 興味のある友達もこのレポートを参照するかもしれません.
非アルコール性脂肪肝臓に関する参照材料
1. Teng-Cing Huang et al. 非アルコール脂肪肝臓. 家庭医学と一次医療, 2015; 30 (11): 314-319.
2. Ching-feng suet al. 非アルコール性脂肪肝疾患の診断と治療. 2015; 30 (11) : 255-260.
3. Ying-Tao Wu et al. 非アルコール性脂肪肝疾患の治療の紹介. Pharmaceutical Journal, 2018; 34 (2) : 27-32.
4. Huei-Wun Liang: 脂肪肝疾患は逆転し、脂肪肝臓に別れを告げることができます! 肝臓病予防 & 治療研究財団のウェブサイト.
終わり
著者について/Mさん. 呉廷耀
ウー・ティンヤオ氏は、以来、霊芝に関する直接の情報を報告し続けている。 1999. 彼女はの著者です 霊芝による治癒 (4月に人民医学出版社に出版 2017).
★この記事は著者の独占的な許可を得て掲載されています.
★上記作品は転載禁止です, 著者の許可なく抜粋または他の方法で使用される.
★上記記載事項に違反した場合, 著者は関連する法的責任を追及します.
★この記事の原文はWu Tingyaoが中国語で執筆し、Alfred Liuが英語に翻訳しました。. 翻訳に齟齬があった場合 (英語) そしてオリジナル (中国語), 本来の中国人が勝つだろう. 読者に質問がある場合, 原作者に連絡してください, MS. 呉廷耀.



