
Benefits ofマンネンタケ extract on patients with Parkinson’s disease
“Can マンネンタケ relieve the symptoms of patients with Parkinson’s disease?」これは多くの患者の質問です, 彼らの家族, 親族や友人は尋ねたいと思っています.
In a report published inSinica Pharmacological Act 4月 2019, ビアオチェン監督が率いる研究チーム, Xuanwu病院の神経学部教授, キャピタルメディカル大学, mentioned that they observed 300 ランダム化されたパーキンソン病患者, 二重盲検, プラセボ対照臨床試験:
These patients ranged from stage 1 (“symptoms appear on one side of the body but do not affect balance”) to stage 4 (“severely impaired mobility but is able to walk and stand independently”). The researchers let the patients take 4 グラムの マンネンタケ extract orally every day for 2 年, and found that the patients’ “motor symptoms” can indeed be relieved by the intervention of マンネンタケ.
So-called motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
◆ Tremor: Uncontrollable shaking of limbs.
◆ Limb stiffness: Continuous tightening of muscles due to increased tension, making limbs difficult to move.
◆ Hypokinesia: Slow movement and inability to perform consecutive movements or perform different movements simultaneously.
◆ Unsteady posture: バランスを崩して転びやすい.
取る マンネンタケ extract every day can slow down the deterioration of these symptoms. Even if there is still a long way to go to cure the disease, it is conceivable that the quality of life of patients with Parkinson’s disease can be improved.


マンネンタケ extract slows the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which is related to the protection of dopamine neurons.
The research team of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University has found through animal experiments that daily oral administration of 400 mg/kg マンネンタケ extract can maintain better motor performance in mice with Parkinson’s disease. The number of dopamine neurons in the brains of mice with Parkinson’s disease is more than double that of mice without マンネンタケ protection (詳細はこちら, see “Professor Biao Chen’s team from Beijing Xuanwu Hospital confirmed that マンネンタケ protects dopamine neurons and relieves symptoms of Parkinson’s disease”).
Dopamine secreted by dopamine neurons is an indispensable neurotransmitter for the brain to regulate muscle activity. The mass death of dopamine neurons is what causes Parkinson’s disease. どうやら, マンネンタケ slowed the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which was associated with less damage to dopamine neurons.
The root cause of the abnormal death of dopamine neurons is that a large number of toxic proteins have accumulated in the substantia nigra of the brain (the main brain area where dopamine neurons are located). In addition to directly threatening the survival and function of dopamine neurons, these proteins will also activate microglia (immune cells resident in the brain) around nerve cells, causing them to continuously secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines to damage dopamine neurons.
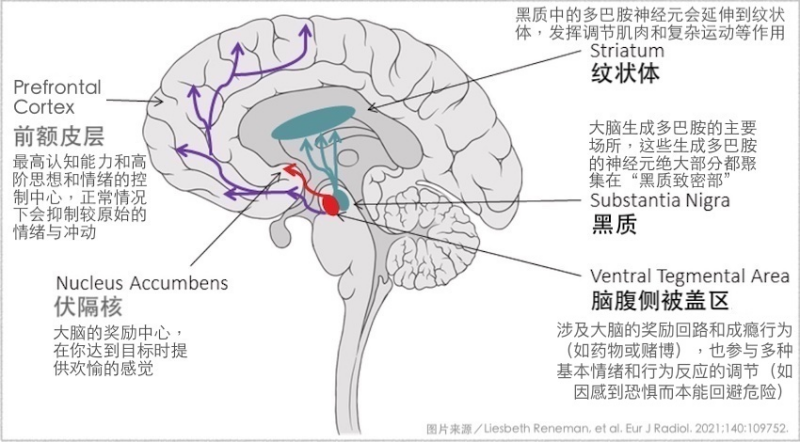
▲The neurons that generate dopamine in the brain are located in the compact part of the “substantia nigra”. The dopamine generated here will be sent to various regions of the brain to play a role along with the extended antennae of the dopamine neurons. The typical movement disorder of Parkinson’s disease is mainly due to the lack of dopamine transported from the substantia nigra to the striatum. Therefore, whether it is dopamine neurons located in the substantia nigra or tentacles of dopamine neurons extending to the striatum, their number and surrounding environment are critical to the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
以前, the research team of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University has confirmed that マンネンタケ extract can reduce the risk of dopamine neuron damage from the injury-resisting pathway by protecting the mechanism of action of mitochondria (cell generators) in the environment of inflammatory response (詳細はこちら, see “Professor Biao Chen’s team from Beijing Xuanwu Hospital confirmed that マンネンタケ protects dopamine neurons and relieves symptoms of Parkinson’s disease”).
In September 2022, the team’s research published in栄養素 further confirmed thatマンネンタケ extract can reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines through the mechanism of “inhibiting the excessive activation of microglia”, thereby protecting dopamine neurons from the damage-reducing pathway.
Mice with Parkinson’s disease who ateマンネンタケ extract had fewer activatedmicroglia in the substantia nigra and striatum.
According to this newly published report, mice were first injected with neurotoxin MPTP to induce human-like Parkinson’s disease, and then 400 mg/kg マンネンタケ extract GLE was orally administered every day from the next day (パーキンソン病 + マンネンタケ extract group) while untreated mice with Parkinson’s disease (only injected with MPTP) and normal mice were used as experimental controls.
後 4 週, a large number of activated microglia appeared in the striatum and substantia nigra pars compacta (the main distribution area of dopamine neurons) in the brain of mice with Parkinson’s disease, but this did not happen in the mice with Parkinson’s disease who ate マンネンタケ extract every day – their condition is closer to that of normal mice (下の写真).
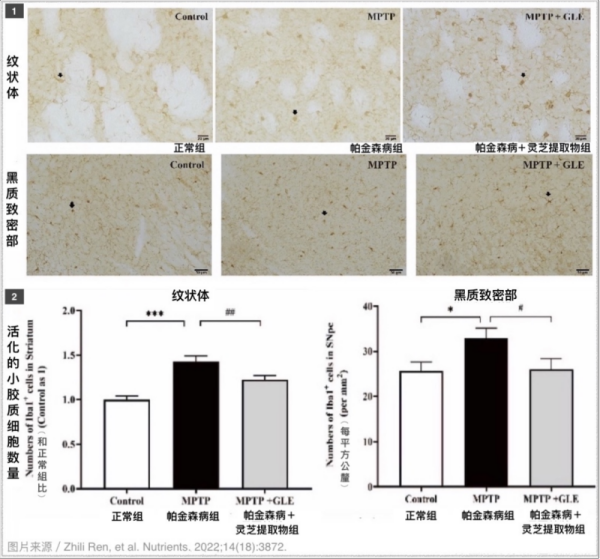
▲ [説明] マンネンタケ has inhibitory effect on microglia in the brain region where the dopamine neurons are located (striatum and substantia nigra pars compacta) in mice with Parkinson’s disease. 形 1 is the stained image of activated microglia in tissue sections, と図 2 is the quantitative statistics of activated microglia.
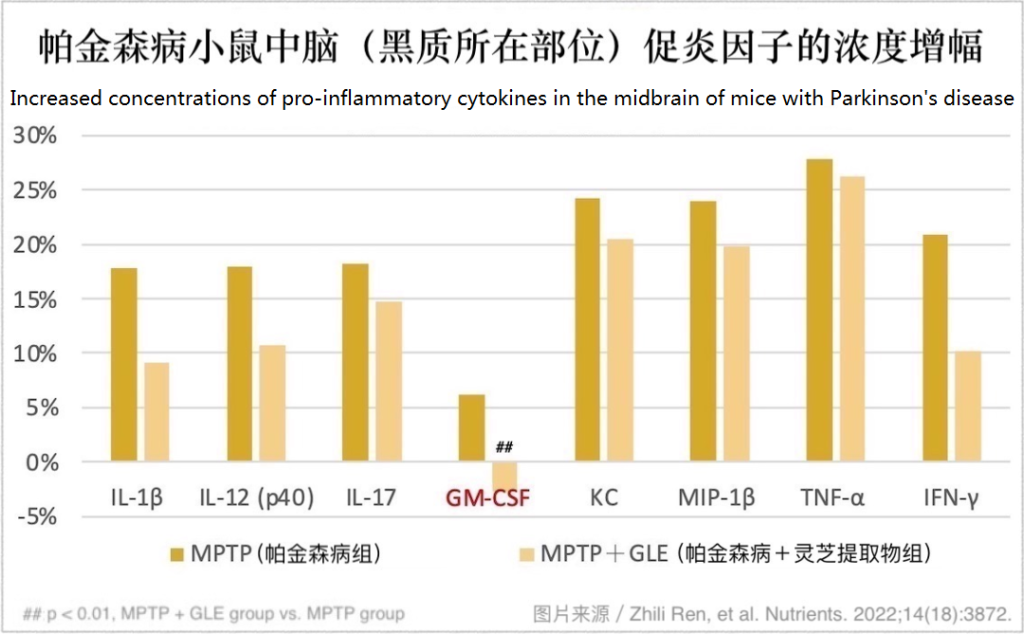
Mice with Parkinson’s disease who ateマンネンタケ extract had lower concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the midbrain and striatum.
Activated microglia cells secrete a variety of cytokines or chemokines to promote inflammation and aggravate the damage of dopamine neurons. しかし, in the detection of the midbrain and striatum of the above-mentioned experimental animals, the researchers found that daily consumption of マンネンタケ extract can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that are significantly increased due to the onset of Parkinson’s disease (下の図に示すように).
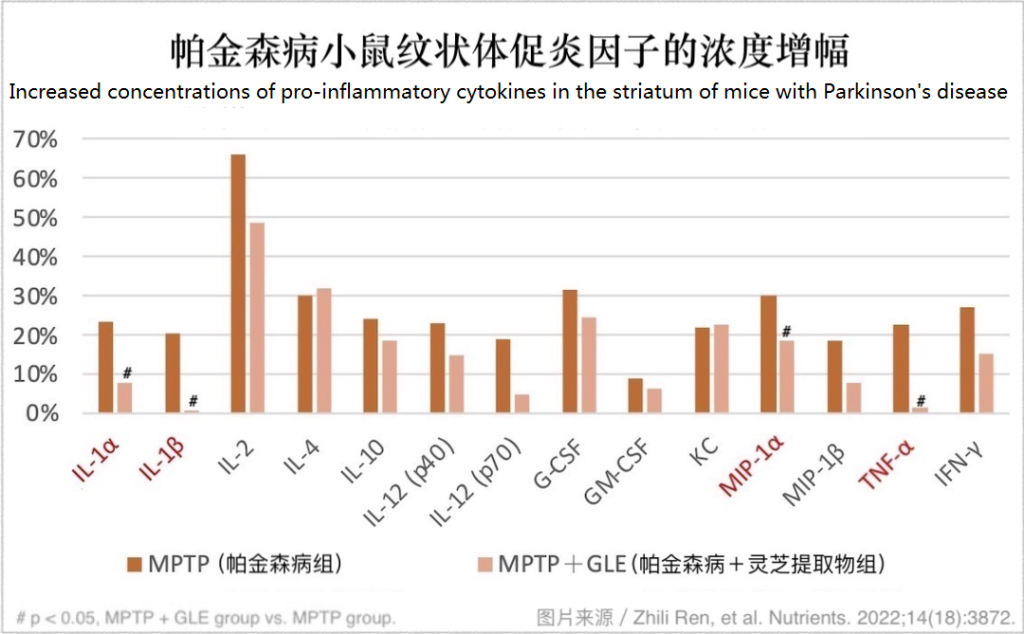
マンネンタケ extract helps delay the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which is the result of the interaction of multiple active ingredients.
The scientific community has confirmed that inflammatory response caused by abnormal activation of microglia is behind the accelerated death of dopamine neurons and the deterioration of Parkinson’s disease. したがって, inhibition of microglia activation by マンネンタケ extract undoubtedly provides an important explanation for why マンネンタケ extract can alleviate the course of Parkinson’s disease.
What are the components ofマンネンタケ that exert these functions?
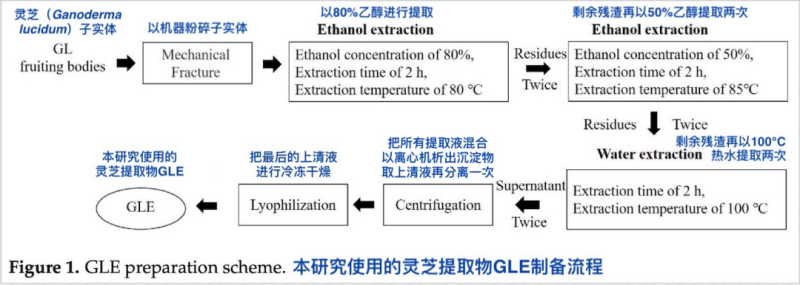
の マンネンタケ extract GLE used in this research is made from the fruiting bodies of マンネンタケ through multiple ethanol and hot water extraction processes. It contains about 9.8% G明瞭な陰皮 多糖類, 0.3-0.4% ganoderic acid A (one of the most important triterpenoids in マンネンタケ 子実体) そして 0.3-0.4% エルゴステロール.
Some related studies in the past have proved that the polysaccharides, トリテルペン, and ganoderic acid A in マンネンタケ all have the functions of “regulating inflammatory response” and “protecting nerve cells”. したがって, researchers believe that the effect of マンネンタケ on delaying the progression of Parkinson’s disease is not the result of the action of a single component but the result of the coordination of multiple components of マンネンタケ 体の中で.
It may never be clear how the various マンネンタケ components eaten in the stomach cross the “blood-brain barrier” and then exert their effects on the microglia and dopamine neurons in the brain. But in any case, it is an indisputable fact that マンネンタケ components can intervene in the pathogenesis to delay the progression of the disease.
The degeneration of dopamine neurons that causes Parkinson’s disease is not a one-step process but a progressive process that degrades a little every day. Faced with this disease that cannot be ended and can only be marathoned with it for a lifetime, patients can only work harder every day in order to pray for less regression every day.
したがって, instead of waiting for the new medicine that turns the world around, it is better to seize the time and take the treasure handed down in front of you and try it bravely. It should not be a dream to reproduce the above-mentioned clinical test results summarized from 300 patients by eating a sufficient amount of マンネンタケ 長い間.

ソース:
1. Zhili Ren, 他。マンネンタケ Modulates Inflammatory Responses following 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) Administration in Mice. Nutrients. 2022;14(18):3872. 土肥: 10.3390/nu14183872.
2. Zhi-Li Ren, 他。マンネンタケ Extract Ameliorates MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism and Protects Dopaminergic Neurons from Oxidative Stress via Regulating Mitochondrial Function, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(4):441-450. 土肥: 10.1038/s41401-018-0077-8.
3. Ruiping Zhang, 他。マンネンタケ Protects Dopaminergic Neuron Degeneration through Inhibition of Microglial Activation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:156810. 土肥: 10.1093/ecam/nep075.
4. Hui Ding, 他。マンネンタケ extract protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting microglial activation. Acta Physiologica Sinica, 2010, 62(6): 547-554.

★この記事は著者の独占的な許可を得て掲載されています, その所有権はガノハーブに属します.
★上記作品は転載禁止です, GanoHerb の許可なく抜粋または他の方法で使用される.
★作品の使用を許諾した場合, 許可の範囲内で使用し、出典を示す必要があります。: ガノハーブ.
★上記記載事項に違反した場合, GanoHerb は関連する法的責任を追及します.
★この記事の原文はWu Tingyaoが中国語で執筆し、Alfred Liuが英語に翻訳しました。. 翻訳に齟齬があった場合 (英語) そしてオリジナル (中国語), 本来の中国人が勝つだろう. 読者に質問がある場合, 原作者に連絡してください, MS. 呉廷耀.



