2017年10月/ディクル大学/Korean Journal of Neurotrauma
文/呉廷耀

過去に, 事故により外傷性脳損傷を負った人もいると聞いた. 定期的な治療を受けることに加えて、, 彼らもたくさん取ったマンネンタケ. 結果として, 回復のスピードと効果は予想を超えていた. 第63号 (春 2014) の “健康な霊芝” 微生物文化教育財団発行の「微生物学教育財団」でも、6つの実際の活用事例が紹介されています。マンネンタケ 交通事故によって引き起こされたトラウマを回復するために.
はマンネンタケ それで “魔法の”? に掲載されたレポート “韓国神経外傷ジャーナル” (韓国神経外傷ジャーナル) 10月にトルコのディクル大学によって 2017 の多糖類抽出物が動物実験で確認されています。マンネンタケ 子実体は確かに脳外傷の回復を促進する可能性がある, その作用機序は酸化ストレスの軽減と炎症の抑制に関連しています。.
研究者たちは人工的な方法を使用しました。 “高所から落ちる” ラットに脳損傷を引き起こす. そのうちの半分は (16 ネズミ) 何も治療を受けなかった (脳外傷グループ). 残りの半分 (脳外傷 +マンネンタケ グループ) を与えられましたマンネンタケ所定の1日用量でm 20 体重1キログラムあたりのmL 30 外傷から数分後 (各mLマンネンタケ 水抽出物が含まれています 2 多糖類のmg). ラットの脳外傷を7日後に評価する. 実験には正常なラットも使用されました (対照群) と通常のラットに餌を与えたマンネンタケ 多糖類(マンネンタケ グループ) 前の 2 つのグループと比較する.
脳内の出血は炎症を引き起こす可能性があります, 脳内の酸化圧を高める (抗酸化酵素が減少してしまう, そしてフリーラジカルの数が増加します), 浮腫みの原因にもなる (脳組織を圧迫して損傷する). 本来の血液脳関門 (脳への異物の侵入をブロックできる、血管と脳の間にある自然の障壁) も破壊されるだろう, より多くの白血球が脳に浸潤するか、脳感染症を引き起こす, 炎症をさらに深刻にする.
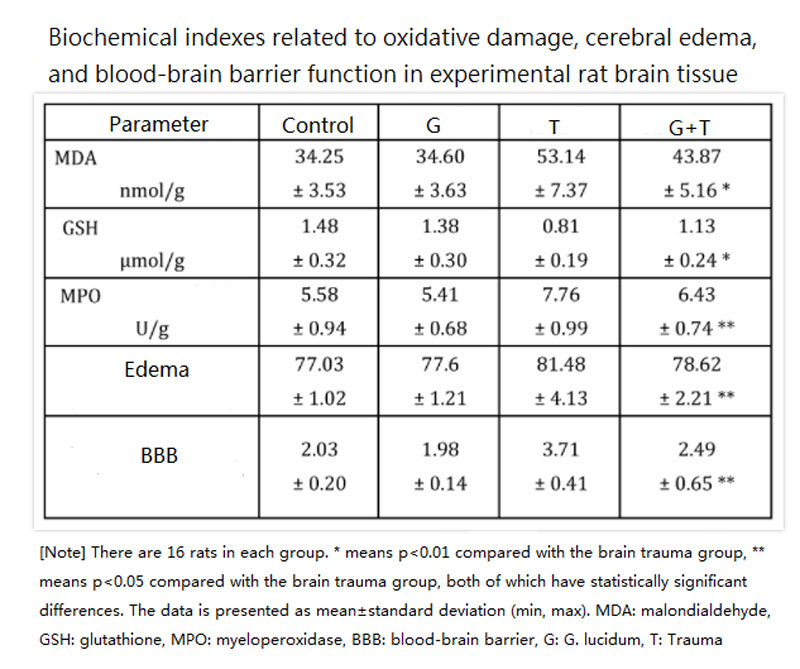
これらの状態は外傷からの脳組織の回復に役立ちません. しかし、この報告書にある動物実験の結果によると、, 脳に損傷を負ったラットを治療した後、マンネンタケ 7日間の多糖類, 彼らの脳組織はフリーラジカルによる損傷が少ない (MDA が減少します), 脳内のフリーラジカルを中和する抗酸化酵素GSHが増加します。, 白血球の炎症はそれほど深刻ではありません (ペルオキシダーゼMPOの分泌が少なくなる), cerebral edema is also significantly improved, and the permeability of the blood-brain barrier is also closer to normal— all values are significantly different from those of brain-traumatized rats that have not received any treatment (下の表を参照してください).
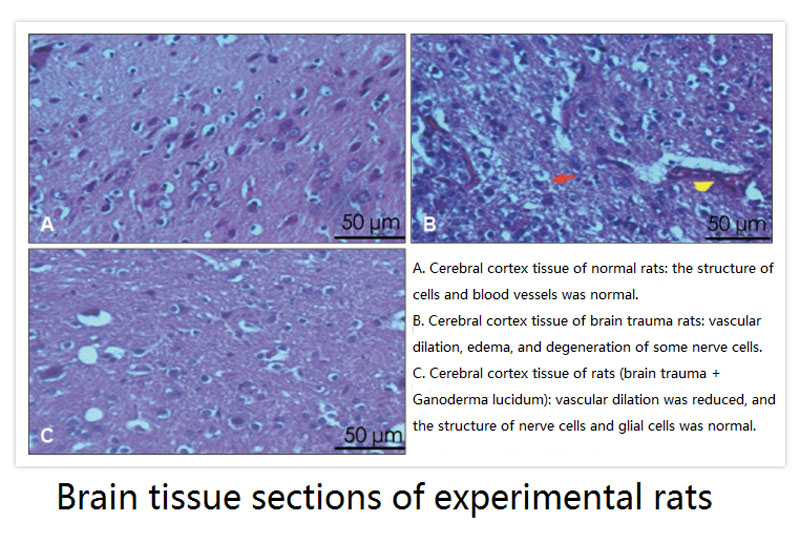
加えて, it can be seen from the tissue sections of the cerebral cortex thatマンネンタケ polysaccharides can improve blood vessel dilation and edema, repair nerve cells, and accelerate the recovery of the injured brain (以下に示すように). The cerebral cortex refers to a connected skin-like structure with many wrinkles wrapped in the outer layer of the brain. It is responsible for higher-level feelings and thinking abilities. したがって, the recovery of this area is of great significance.
The researchers also tested three other important indicators in rat brain tissue, プロテインキナーゼp38 MAPKを含む, それは炎症と正の関係があります, 血管内皮増殖因子 (VEGF), 血管構造を修復するために必要です, とミクログリア細胞, 損傷した神経細胞や病原体を除去する役割を果たします.
判明したのは、, 脳に損傷を受けて何も食べなかったラットとの比較マンネンタケ 多糖類, ただし、p38 MAPK の活性は、脳に損傷を与えたラットで検出されました。マンネンタケ 多糖類, (反応は進行中であるが制御されており、悪化しないことを示しています), 血管内皮増殖因子とミクログリア細胞が大幅に増加, それを示しているマンネンタケ 多糖類は脳血管と脳神経の修復と再構築に有益です.
上記の実験結果は、継続投与の効果を示しています。マンネンタケ polysaccharides for seven days after the brain is injured. Researchers believe that if the appropriate dose ofマンネンタケ polysaccharides can be used as adjuvant therapy after brain trauma occurs, it will be very helpful for alleviating inflammation and cerebral edema, or for protecting nerve cells and glial cells.
[ソース] Özevren H, 他. Ganoderma Lucidum protects rat brain tissue against trauma-induced oxidative stress. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017; 13(2): 76-84.
終わり
著者について/Mさん. 呉廷耀
呉廷耀氏は直接報告しているマンネンタケ それ以来の情報 1999. 彼女はの著者です霊芝による治癒 (4月に人民医学出版社に出版 2017).
★この記事は著者の独占的な許可を得て掲載されています
★上記作品は転載禁止です, 著者の許可なく抜粋または他の方法で使用される
★上記記載事項に違反した場合, 著者は関連する法的責任を追及します
★この記事の原文はWu Tingyaoが中国語で執筆し、Alfred Liuが英語に翻訳しました。. 翻訳に齟齬があった場合 (英語) そしてオリジナル (中国語), 本来の中国人が勝つだろう. 読者に質問がある場合, 原作者に連絡してください, MS. 呉廷耀.



