1월 29, 2020 / 후난성 인민병원, 등. / 산화의학과 세포수명
문자/우 팅야오

후난성 인민병원과 후난성 응급 및 중환자 치료 메타보노믹스 핵심 연구소가 "산화의학과 세포 수명"에 발표한 연구에서는 다음과 같이 지적했습니다.영지버섯 트리테르페노이드(GLT) 뇌 신경 세포를 보호하고 알츠하이머병으로 인한 인지 장애를 줄일 수 있습니다. (광고) 항세포사멸과 같은 메커니즘을 통해, 항산화, 그리고 항신경섬유엉킴.
영지버섯 트리테르페노이드는 알츠하이머병 환자의 인지 저하를 지연시킵니다.
첫 번째, 연구원들에게 먹이를 주다영지버섯 트리테르페노이드 (GLT) 알츠하이머병에 (광고) 초기 증상이 나타난 쥐. 60일 후, 그들은 Morris Water Maze로 쥐의 인지 능력을 테스트했습니다. (MWM).
선천적으로 물을 싫어하는 생쥐의 특성을 이용하여 항상 물을 피할 수 있는 곳을 찾으려고 노력합니다., 연구진은 Morris Water Maze를 실시했습니다., 큰 원형 수영장에 휴식용 플랫폼을 설치하여 생쥐가 헤엄치는 거리와 휴식용 플랫폼을 찾는 데 소요되는 시간을 쥐의 인지 능력을 판단하는 지표로 계산하는 것입니다.. 쥐가 휴식 플랫폼을 찾지 못한 경우 (2분 안에), 연구원들은 쥐를 플랫폼으로 안내하는 데 도움을 줄 것입니다.
물에 들어가는 시작점은 매번 다르지만, 일반 쥐는 일상적인 경험을 통해 여전히 빠르게 휴식 플랫폼을 찾을 수 있습니다.. 이러한 실험은 하루에 한 번씩 총 9일 동안 진행되었다.. 모든 점수를 평균으로 계산, 연구자들은 AD 쥐가 (광고그룹) 일반 쥐보다 2배의 시간을 보내거나 3/4의 시간을 더 오래 수영해야 합니다. (대조군) 쉴 곳을 찾으러, 이는 AD 쥐의 뇌 인지 기능이 크게 저하되었음을 나타냅니다..
하지만, 고용량을 먹인 AD 쥐 (1.4g/kg/일) 의 GLT는 정상 쥐와 AD 쥐와 휴식 플랫폼을 찾는 데 거의 동일한 시간과 수영 거리가 걸렸습니다. (서양의학 대조그룹) 매일 도네페질을 먹인다(그림 1~2).
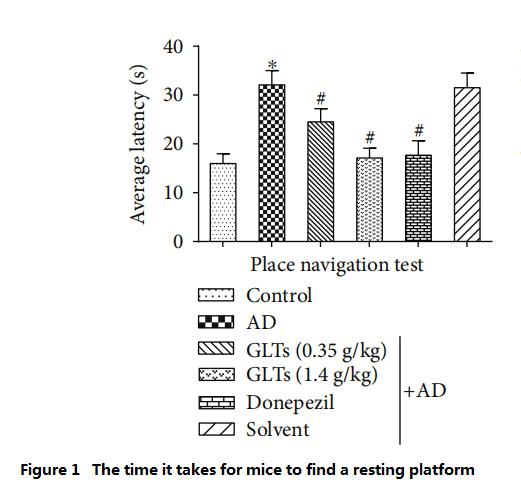
(소요시간이 적을수록, 인지능력이 좋을수록)
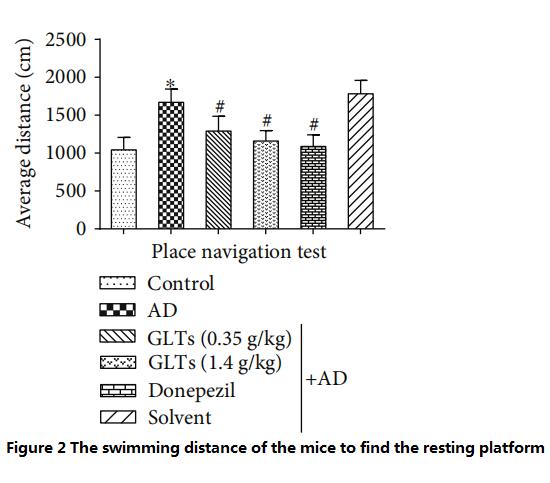
(필요한 거리가 짧을수록, 인지능력이 좋을수록)
위 실험 종료 후 다음날, 연구진은 수영장에서 휴식 플랫폼을 제거하고 생쥐를 물에 2분 동안 넣었습니다..
지난 9일간의 경험으로 인해, 정상적인 쥐는 플랫폼의 원래 위치를 기억하고 "사라지는 플랫폼"을 찾기 위해 원래 위치 주변을 수영하는 데 더 많은 시간을 보냈고, 알츠하이머병 쥐는 목표 없이 헤엄쳤습니다..
대조적으로, GLT로 보호된 알츠하이머 쥐는 저용량에서도 정상 쥐처럼 행동했습니다. (0.35 g/kg/일) 또는 고용량 (1.4 g/kg/일) 서양 의학을 먹인 MD 쥐와 거의 같은 점수를 얻었습니다. (피규어 3 에게 4).
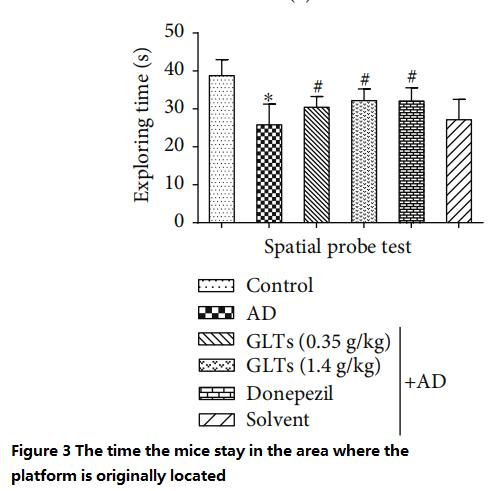
(체류 기간이 길어질수록, 인지능력이 좋을수록)
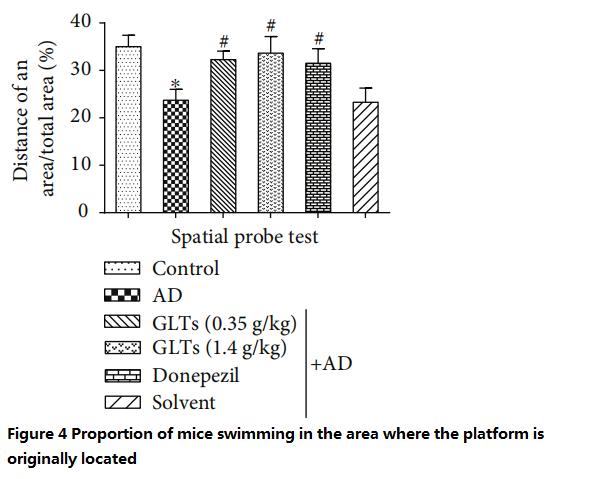
(비율이 높을수록, 인지능력이 좋을수록)
영지버섯 트리테르페노이드는 신경 세포의 완전성을 유지합니다.
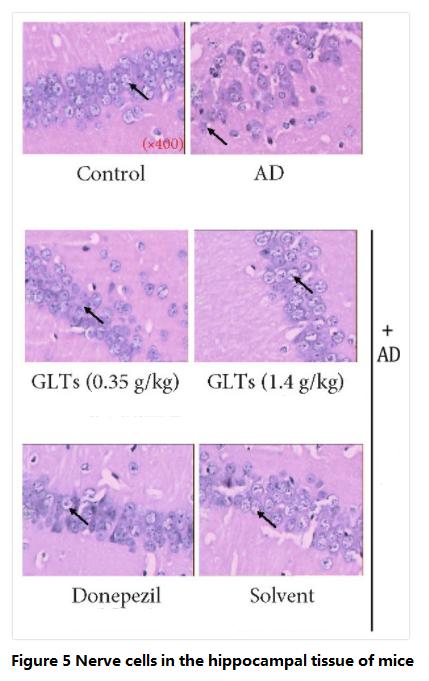
학습 및 기억 능력 감소는 가장 초기의 인지 기능 저하입니다. (무질서) 알츠하이머병 환자의 경우, 그리고 이 기능을 담당하는 신경세포는 해마회에 위치합니다.. 그러므로, 연구진이 위의 실험을 완료한 후, 그들은 추가 조사를 위해 쥐의 뇌를 해부했습니다.
그 결과, 정상 쥐의 해마회 신경세포가 가지런히 배열되어 있는 것으로 나타났다., 균일한 크기, 규칙적인 외모, 세포막과 핵의 경계가 명확하게 구분되어 있습니다.; AD 쥐의 해마이랑 신경세포가 무질서하게 배열되어 있다, 크기가 다르다, 외모가 불규칙하다, 개체수가 대폭 감소, 그 구조는 분명히 손상되었습니다.
하지만, 이 상황은 Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids를 섭취하는 AD 쥐에서는 나타나지 않았습니다.. 해마이랑의 신경 세포는 여전히 높은 수준의 무결성을 유지하고 있습니다., 그리고 뚜렷한 세포 괴사는 없었습니다., 것을 나타내는영지버섯 트리테르페노이드는 해마이랑에 보호 효과가 있었습니다 ( 수치 5).
영지버섯 트리테르페노이드는 신경섬유매듭을 감소시킵니다..
동시에, 연구자들은 또한 대뇌 피질의 신경원섬유 엉킴의 수가 (장기기억 저장) AD 마우스의 해마 이랑 조직은 다음과 같이 보호됩니다.영지버섯 트리테르페노이드 수치는 치료받지 않은 AD 마우스의 수치보다 현저히 낮았습니다. (수치 6).
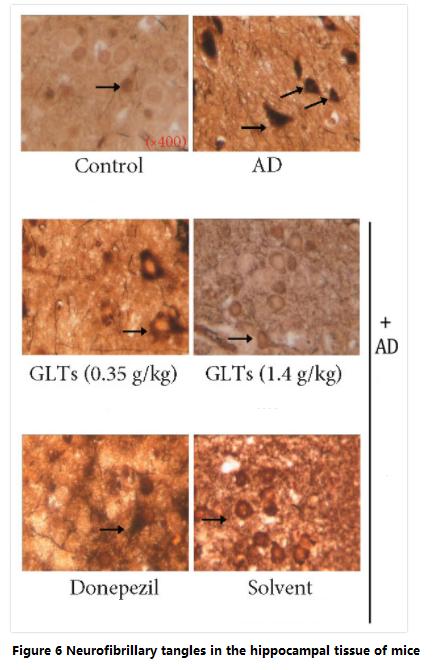
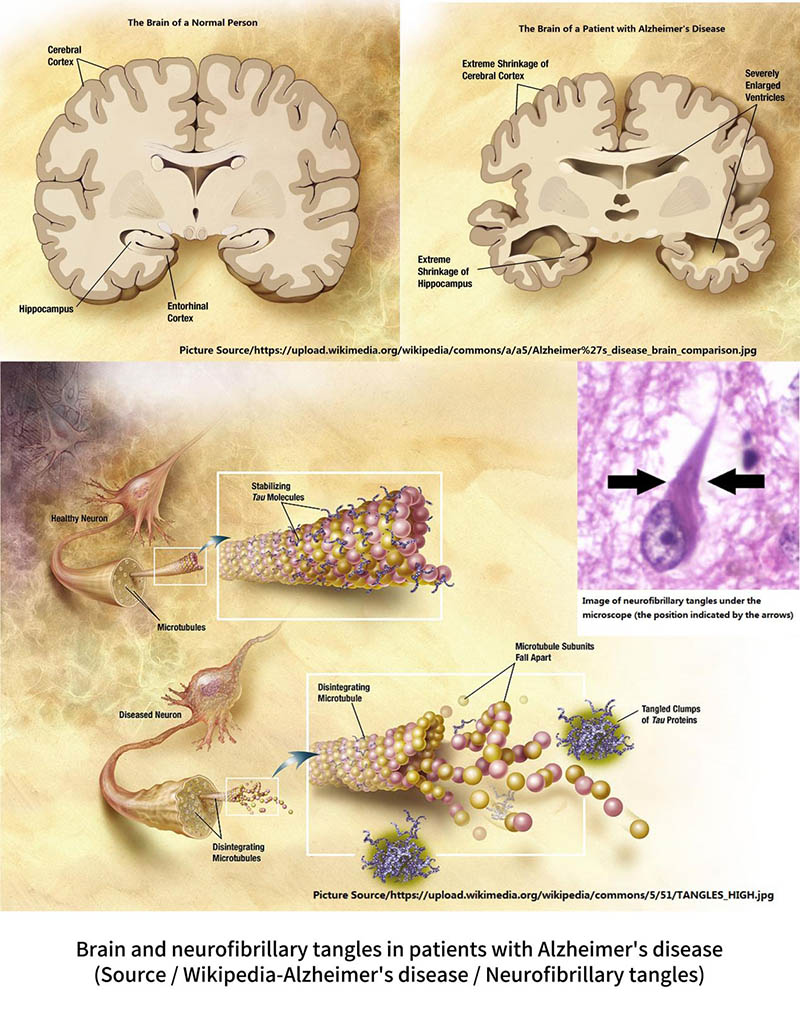
신경섬유매듭은 알츠하이머병의 주요 증상 중 하나입니다.. 세포 외부에서 발생하는 아밀로이드 침전물과 달리, 신경섬유매듭은 '타우 단백질'의 돌연변이로 인해 신경세포에서 발생합니다..
정상적인 상황에서는, 타우 단백질이 세포골격에 결합 (미세소관) 세포골격의 형성과 안정성을 돕기 위해. 하지만, 알츠하이머병 환자의 뇌에 있는 타우 단백질이 돌연변이를 일으키고 세포골격에 결합할 수 없습니다.. 결과적으로, 타우 단백질은 클러스터로 응집되어 소위 "신경원섬유 엉킴"을 형성합니다., 세포에 축적되어 세포의 기능을 방해하는 물질입니다.. 타오 단백질이 부족한 세포골격은 점차적으로 왜곡되고 분해됩니다., 세포 사멸로 이어지는.
신경원섬유엉킴의 수는 알츠하이머병의 악화 정도를 반영합니다.. 그러므로, Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids는 신경섬유매듭의 형성을 억제할 수 있습니다., 이는 중요한 메커니즘 중 하나가 되어야 합니다.영지버섯 알츠하이머병의 인지 저하를 지연시키는 트리테르페노이드.
영지버섯 트리테르페노이드는 신경 세포의 세포사멸을 감소시킵니다.
β-아밀로이드 침착 또는 신경원섬유 엉킴은 세포의 자살 프로그램을 시작하고 신경 세포의 세포사멸을 촉진합니다.. 신경세포가 더 많이 죽으면, 더 많은 기능이 손실됨, 알츠하이머병으로 인한 인지 저하가 더욱 심해집니다..
각 실험쥐군의 해마이랑 조직 분석에서, AD 쥐의 신경세포 사멸률은 같은 연령의 정상 쥐에 비해 4배 이상 높은 것으로 나타났다.; 고용량임에도 불구하고영지마명쾌함 트리테르페노이드는 신경 세포의 비정상적인 세포사멸을 완전히 예방할 수 없습니다., 그들은 피해를 절반으로 줄일 수 있었습니다, 그 효과는 서양의학과 비슷하다. (수치 7).
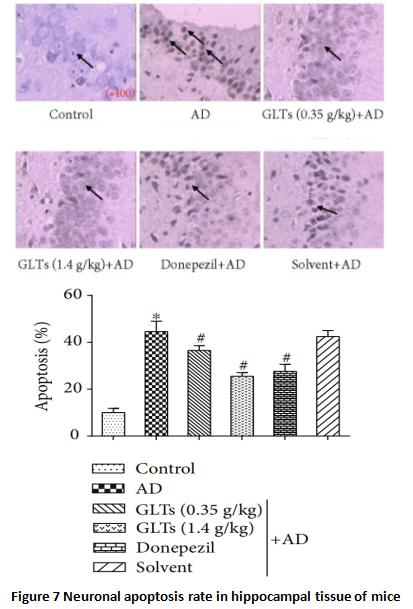
연구진은 추가로 분석한 결과 AD 쥐의 경우영지버섯 트리테르페노이드, 뇌신경세포는 베타아밀로이드 단백질로 인한 산화적 손상에 맞서기 위해 강력한 항산화 메커니즘을 가지고 있으며, 세포사멸 메커니즘은 쉽게 활성화되지 않습니다.. 다시 말해서, Ganoderma lucidum triterpenes는 뇌 신경 세포의 스트레스 저항성을 강화합니다., 가혹한 환경에서 더 잘 생존하고 작동할 수 있도록 만듭니다..
영지버섯 다당류도 유용합니다.
위의 연구 결과는영지버섯 트리테르페노이드, 식도를 통해 위장관으로 들어간 후, 항산화를 통해 알츠하이머병의 진행을 늦출 수 있습니다, 항아폽토시스, 그리고 항신경섬유엉킴.
사실은, 효과영지버섯 다당류는 Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids보다 약하지 않습니다.. ~ 안에 2017, 통지대학교와 중국과학원이 공동으로 "줄기세포 보고서"에 발표한 연구에 따르면영지버섯 물 추출물 또는영지버섯 다당류는 AD 쥐의 뇌에서 베타-아밀로이드 침착을 감소시킬 수 있습니다, 해마이랑의 신경 전구 세포의 증식을 돕고 학습 및 기억력 저하를 늦춥니다.. (자세한 내용은, 보다: Ganoderma lucidum 다당류에스 알츠하이머병으로 인한 인지 저하 감소)
영지버섯 트리테르페노이드 및영지버섯 다당류는 알츠하이머병으로 인한 뇌를 보호하는 데 다양한 효과를 갖는 것으로 보입니다. 두 가지 병용요법으로 알츠하이머병 진행 속도 늦출 수 있을까?
알츠하이머병이 발생하면, 그것을 되돌리기는 어렵다. 하지만, 우리가 더 많은 인지 능력을 유지할 수 있다면, 학습과 기억을 포함한, 우리의 제한된 삶 속에서, 알츠하이머병이 나아질 기회가 있을지도 모릅니다.
원천
1. 유 엔, 외. 영지버섯 트리테르페노이드 (GLT) APP/PS1 형질전환 알츠하이머병 마우스에서 ROCK 신호 경로의 억제를 통해 신경세포 사멸 감소. 셀 수명이 긴 산화물. 2020; 2020: 9894037.
2. 황 S, 외. 다당류 영지버섯 알츠하이머병 마우스 모델에서 인지 기능 및 신경 전구 세포 증식 촉진. 줄기세포 보고서. 2017 1월 10;8(1):84-94. 도이: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.12.007.
끝
저자 소개 / 씨. 우팅야오
Wu Tingyao가 직접 보고해 왔습니다.영지버섯 이후의 정보 1999. 그녀는 다음의 저자입니다.Ganoderma로 치유 (4월 인민의학출판사에 게재 2017).
★ 이 글은 저자의 단독 승인 하에 게재되었습니다.
★ 위 작품은 복제할 수 없습니다, 저작자의 허락 없이 발췌하거나 다른 방법으로 사용한 경우
★ 위의 내용을 위반한 경우, 저자는 관련 법적 책임을 추구할 것입니다.
★ 이 기사의 원문은 Wu Tingyao가 중국어로 작성하고 Alfred Liu가 영어로 번역했습니다.. 번역 내용에 차이가 있는 경우 (영어) 그리고 원본 (중국인), 원래 중국어가 우선합니다. 독자들이 궁금한 점이 있으면, 원작자에게 연락주세요, 양. 우팅야오.



